Tardigrades, also known as water bears, are microscopic animals that have captured the fascination of scientists and the public alike. These resilient creatures can survive in some of the harshest conditions on Earth, from freezing temperatures to extreme radiation. In this article, we will explore the incredible abilities and adaptations that make tardigrades such unique and fascinating organisms.
Mục lục
- 1. Introduction: Meet the Tardigrades – Nature’s Microscopic Marvels
- 2. Tardigrade Habitats: From Your Backyard to the Depths of the Ocean
- 3. Related articles 01:
- 4. Tardigrades and Human Significance
- 5. Tardigrade Research Breakthroughs Up to Date
- 6. Related articles 02:
- 7. The Importance of Tardigrade Conservation: Protecting a Unique Species
- 8. Conclusion
Introduction: Meet the Tardigrades – Nature’s Microscopic Marvels
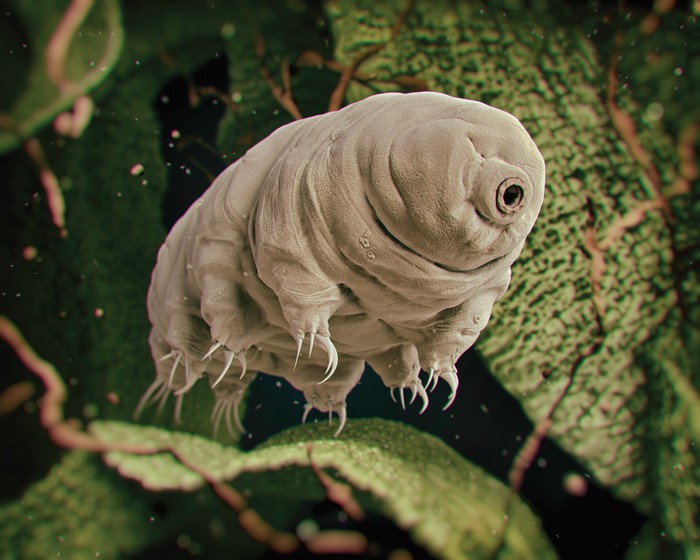

Tardigrades, also known as water bears, are microscopic creatures renowned for their remarkable ability to survive some of the most extreme conditions on Earth. These resilient micro-beasts, typically measuring between 0.3 and 0.5 millimeters, have fascinated scientists and science enthusiasts alike due to their unique characteristics and unparalleled resilience.
Anatomy and Characteristics
Tardigrades are small animals, typically less than 1mm in length. They have four pairs of legs with claws at the end, giving them a bear-like appearance – hence their nickname “water bears.” They are found in diverse habitats around the world, including oceans, forests, and even the Antarctic.
Aside from their adorable appearance, tardigrades possess some incredible characteristics that make them stand out from other organisms. For instance, they have no respiratory system and can survive for long periods without food or water. They also have a primitive type of nervous system and can withstand extreme environmental conditions.
Tardigrade Reproduction and Life Cycle
Tardigrades reproduce through a process called parthenogenesis, where females can produce offspring without the need for male fertilization. However, sexual reproduction also occurs, with some species requiring a mate. During sexual reproduction, males deposit sperm into the female’s cloaca, fertilizing the eggs internally. The female then lays the fertilized eggs into the environment.
The life cycle of a tardigrade begins with the egg, which hatches after a period ranging from a few days to several weeks, depending on environmental conditions. The juvenile tardigrades resemble miniature adults and undergo several molts as they grow, shedding their outer cuticle to accommodate their increasing size. Tardigrades can live from a few months to a couple of years, with some entering a state of cryptobiosis to extend their lifespan during unfavorable conditions.
Tardigrade Habitats: From Your Backyard to the Depths of the Ocean
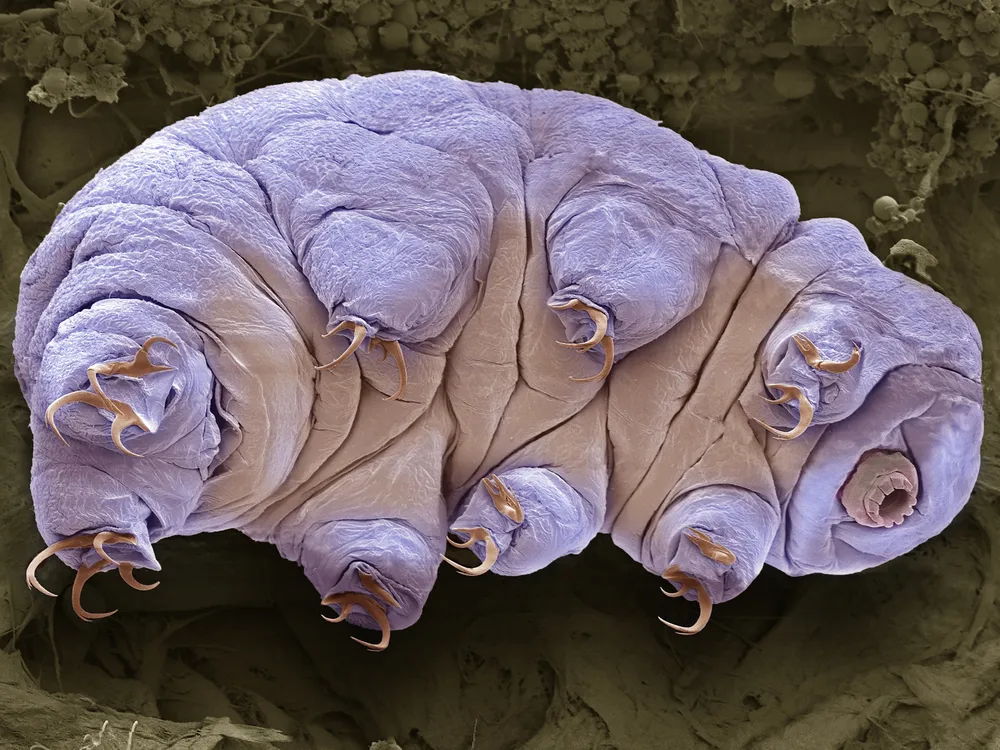
Tardigrades can be found in a variety of environments, from terrestrial to aquatic habitats. They thrive in moss and lichen in your backyard, as well as in the depths of the ocean. Their adaptability allows them to inhabit regions with high pressure, extreme temperatures, and even high levels of radiation. This versatility is one of the key reasons tardigrades have survived for millions of years.
Surviving Extreme Conditions: The Secret to Tardigrades’ Resilience
One of the most astonishing abilities of tardigrades is their ability to survive in some of the harshest conditions on Earth. They can withstand extreme temperatures, ranging from -200°C to 150°C, by entering a state known as cryptobiosis, where all metabolic activity stops and they become almost completely dehydrated.
Tardigrades can also survive in a vacuum for days, withstanding pressures six times greater than those found in the deepest parts of the ocean. In addition to these incredible feats, they can also endure high levels of radiation that would be lethal to most other living organisms.
Tardigrades in Space: The Ultimate Survivors
Perhaps one of the most remarkable demonstrations of tardigrades’ resilience is their ability to survive in the harsh conditions of outer space. In experiments conducted by space agencies, these tiny creatures have been exposed to the vacuum of space, intense solar and cosmic radiation, and extreme temperatures. Remarkably, tardigrades not only survived but also managed to reproduce upon returning to Earth. This ability to endure the conditions of space travel has led scientists to speculate about the potential for life to exist beyond our planet and the possibility of interplanetary panspermia, where life could travel between planets on meteorites or other celestial bodies.
Tardigrades in Scientific Research: Unlocking the Secrets of Survival
The unique abilities of tardigrades have made them of great interest to the scientific community. Researchers are studying these indomitable creatures to understand the molecular and genetic mechanisms behind their resilience. Discoveries in tardigrade biology could potentially lead to breakthroughs in medicine, particularly in areas such as cancer treatment, stress response, and organ preservation.
1. https://dodopet.info/protect-your-furry-friends-the-importance-of-pet-insurance-in-texas-2324/
2. https://dodopet.info/protect-your-purr-fect-companion-with-cat-insurance-2367/
3. https://dodopet.info/the-ultimate-guide-to-pet-insurance-benefits-and-beyond-2328/
4. https://dodopet.info/deer-mouse-discoveries-a-guide-for-wildlife-enthusiasts-2327/
5. https://dodopet.info/the-ultimate-guide-to-dog-insurance-protecting-your-best-friend-2323/
Moreover, the study of tardigrades in space has implications for astrobiology and the possibility of life on other planets. By understanding how tardigrades can survive in the extreme conditions of outer space, scientists gain insights into the potential for life to exist and persist beyond Earth.
Tardigrades and Human Significance
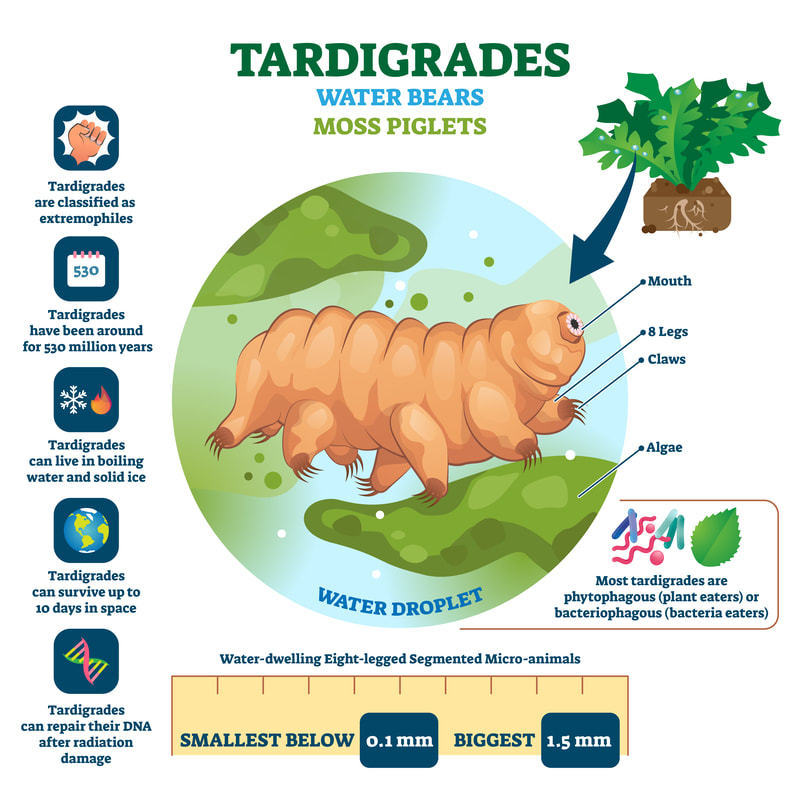
Tardigrades, despite their microscopic size, play a significant role in human interest and scientific research. Their extraordinary resilience and ability to survive extreme conditions have made them subjects of fascination and admiration. Beyond their biological and ecological importance, tardigrades have the potential to contribute to advancements in various scientific fields.
Biotechnology and Medical Applications
One of the most promising areas of research involves the application of tardigrade biology to biotechnology and medicine. Scientists are studying the proteins and genes that enable tardigrades to undergo cryptobiosis, with the aim of developing new methods for preserving biological materials. For instance, these studies could lead to improved techniques for cryopreserving organs, which would be a groundbreaking advancement for organ transplants.
Additionally, insights gained from tardigrade genetics could inform the development of new treatments for diseases. By understanding how tardigrades repair and protect their DNA from radiation damage, researchers hope to uncover novel therapeutic approaches for conditions like cancer, where DNA damage is a critical concern.
Environmental Monitoring and Education
Tardigrades also serve as excellent indicators of environmental health. Due to their sensitivity to changes in their habitats, monitoring tardigrade populations can provide valuable data on the impact of pollution, climate change, and habitat destruction. This makes them useful allies in ecological studies and conservation efforts.
Moreover, the fascinating story of tardigrades’ survival abilities presents an engaging educational opportunity. Teaching about these “water bears” can inspire interest in biology and environmental science among students and the general public. Their incredible adaptations serve as a gateway to broader discussions about biodiversity, evolution, and the resilience of life on Earth.
Future Prospects and Speculations
As we continue to explore the capabilities of tardigrades, their potential to contribute to science and technology remains expansive. The study of their survival mechanisms not only enhances our understanding of life in extreme conditions but also opens up possibilities for future innovations. Whether it is space exploration, biotechnology, or environmental science, tardigrades are proving to be a small but mighty influence on human progress.
In conclusion, tardigrades are much more than just microscopic marvels. Their unique adaptations have far-reaching implications for scientific research and practical applications. By delving into the mysteries of these resilient organisms, we uncover valuable insights that transcend their tiny existence and impact the broader realm of human knowledge.
Tardigrade Research Breakthroughs Up to Date

Although tardigrades have been studied for over 200 years, there is still much to discover about these fascinating creatures. In recent years, significant breakthroughs have shed light on their biology and opened up new possibilities for research.
Horizontal Gene Transfer in Tardigrades
In 2015, scientists discovered that tardigrades possess a unique ability to acquire foreign DNA from other organisms through horizontal gene transfer (HGT). This means that they can incorporate genes from other species into their own genetic code, essentially borrowing traits from other organisms. This discovery challenges the traditional understanding of evolution and has implications for biotechnology and medicine.
The Tardigrade Genome Project
In 2018, an international team of researchers completed the tardigrade genome project, sequencing and analyzing the entire genetic code of a tardigrade species. This project revealed numerous genes responsible for their remarkable survival abilities, including those involved in repairing DNA damage and preserving proteins during stressful conditions.
Uncovering the Secrets of Cryptobiosis
Cryptobiosis, the state of suspended animation that allows tardigrades to survive extreme conditions, has long puzzled scientists. In recent years, studies have focused on understanding how these creatures can enter and exit cryptobiosis without harm. Researchers have identified specific proteins and genes involved in this process, providing insights into potential applications for human medicine.
1. https://dodopet.info/protect-your-purr-fect-companion-with-cat-insurance-2367/
2. https://dodopet.info/deer-mouse-discoveries-a-guide-for-wildlife-enthusiasts-2327/
3. https://dodopet.info/the-ultimate-guide-to-dog-insurance-protecting-your-best-friend-2323/
5. https://dodopet.info/protect-your-furry-friends-the-importance-of-pet-insurance-in-texas-2324/
The Importance of Tardigrade Conservation: Protecting a Unique Species
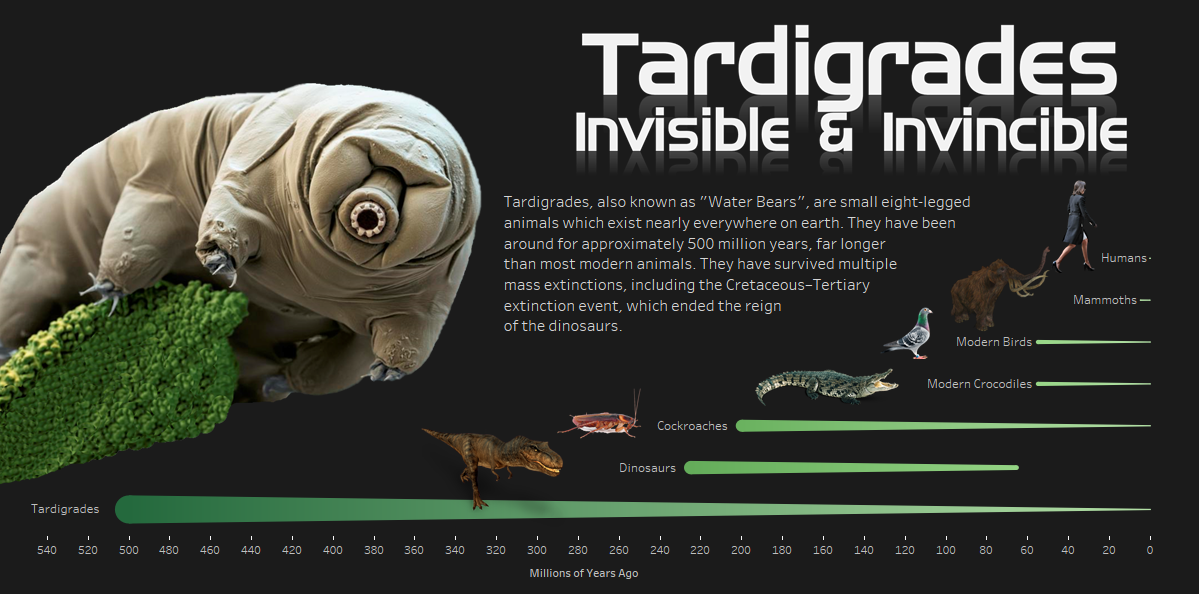
The preservation of tardigrades is crucial for maintaining biodiversity and the continued advancement of scientific research. Though tardigrades are known for their resilience, they still face threats from environmental changes, pollution, and habitat degradation. Protecting their natural habitats ensures that these microscopic organisms can continue to thrive and contribute to ecological balance.
Conservation Efforts and Challenges
Efforts to conserve tardigrades are intrinsically linked to broader environmental conservation initiatives. As tardigrades inhabit a diverse range of ecosystems, including mosses, lichens, and leaf litter, protecting these habitats is essential. Conservation strategies that focus on reducing pollution, curbing climate change, and preserving natural environments indirectly benefit tardigrade populations. However, the microscopic size of tardigrades presents unique challenges for direct conservation efforts. Unlike larger organisms, they are not easily tracked or monitored, making it difficult to assess their population health and apply targeted conservation measures.
The Role of Citizen Science
Citizen science programs offer a valuable avenue for tardigrade conservation. By engaging the public in scientific observation and data collection, researchers can gather extensive information about tardigrade distributions and environmental conditions. Educational initiatives that teach people how to find and identify tardigrades in their local environments can foster greater awareness and appreciation for these organisms. This grassroots approach not only aids scientific research but also cultivates a sense of stewardship for the natural world.
Future Directions in Tardigrade Research and Conservation
Looking ahead, the integration of advanced technologies such as environmental DNA (eDNA) analysis and remote sensing could revolutionize tardigrade research. These tools could provide more accurate assessments of tardigrade populations and their habitats, enabling more effective conservation strategies. Continued exploration into the genetic and physiological adaptations of tardigrades will undoubtedly yield further insights with wide-ranging applications.
The Expanding Role of Citizen Science in Tardigrade Research
Citizen science is emerging as a pivotal force in the study and conservation of tardigrades. By involving non-professional scientists in research efforts, citizen science projects leverage the collective power of enthusiasts and volunteers to gather valuable data that would otherwise be challenging to obtain. This community-driven approach is particularly beneficial for the study of tardigrades, given their microscopic size and widespread distribution.
Programs such as the “Tardigrade Hunters” initiative encourage individuals to collect samples from various environments, including mosses, lichens, and soil. These samples are then analyzed to identify the presence of tardigrades and document their biodiversity. Through online platforms and mobile applications, participants can easily share their findings with researchers, contributing to an expanding database of tardigrade distribution and habitats.
Moreover, educational workshops and outreach events are crucial components of these citizen science efforts. By educating the public about tardigrades and their ecological significance, these programs foster a deeper connection between people and the microscopic world around them. Schools, community groups, and nature clubs are increasingly incorporating tardigrade hunts into their activities, transforming curiosity into actionable scientific endeavors.
The collective data gathered through citizen science has already led to several noteworthy discoveries, including the identification of new tardigrade species and the mapping of their geographical spread. As technology continues to advance, the role of citizen science in tardigrade research is poised to grow, offering an inclusive platform for anyone with an interest in these remarkable creatures to contribute to science and conservation.
Conclusion
The research and conservation efforts surrounding tardigrades highlight the intricate connections within our ecosystems and the importance of protecting even the smallest forms of life. Tardigrades, though microscopic, play a significant role in their environments and offer invaluable insights into biology and resilience. Their ability to survive extreme conditions, such as high radiation and desiccation, positions them as unique biological models for studying stress resistance and potential applications in medicine and biotechnology.
Moreover, the collaborative nature of tardigrade research, involving professional scientists, citizen scientists, and educators, exemplifies the broader societal benefits of scientific discovery and conservation. By promoting awareness and engagement through public participation, we not only enhance our understanding of these fascinating organisms but also foster a culture of stewardship and responsibility towards our environment.
















